LeetCode 24 Swap nodes in pairs
13 Mar 2022the question describe
The question is Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You must solve the problem without modifying the values in the list’s nodes (i.e., only nodes themselves may be changed.)
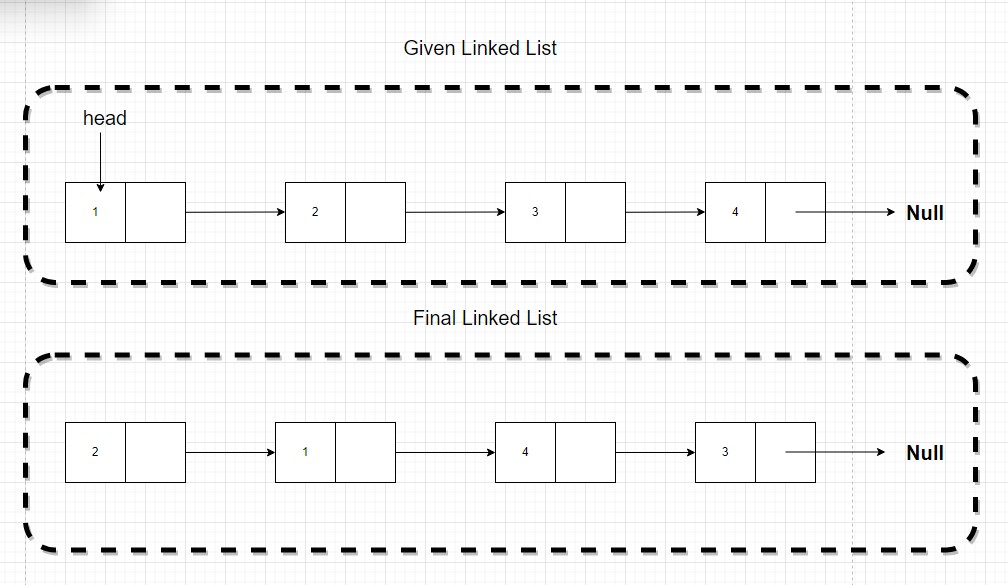
LeetCode will give you a link, you need swap it exactly, like follow pic
Let’s understand the approach
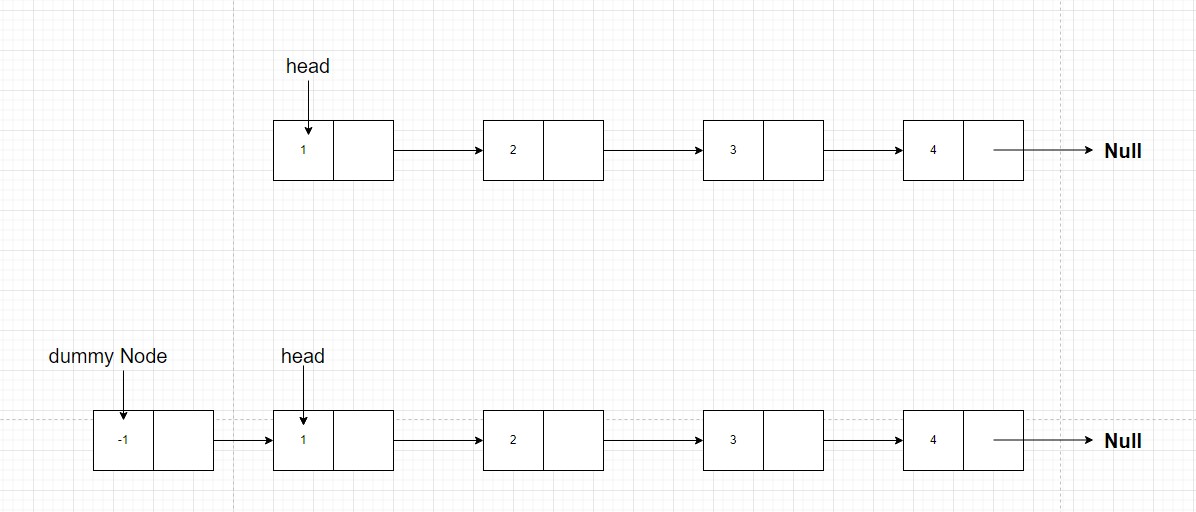
- First, we will place a
dummy nodebefore ahead nodeso that the code we write can be applicable to the head node also, and we don’t have to specifically write different conditions for the head node.
-
Now, let the head be our
n1 nodeand next ben2 node, that meansnode with value 1isn1andnode with value 2isn2, and we have to swapn1andn2. So for this, we will also have to keep track of the node previous ton1 node, let it beprev, as it’s next pointer value will have to change after we swap then1 nodeandn2 node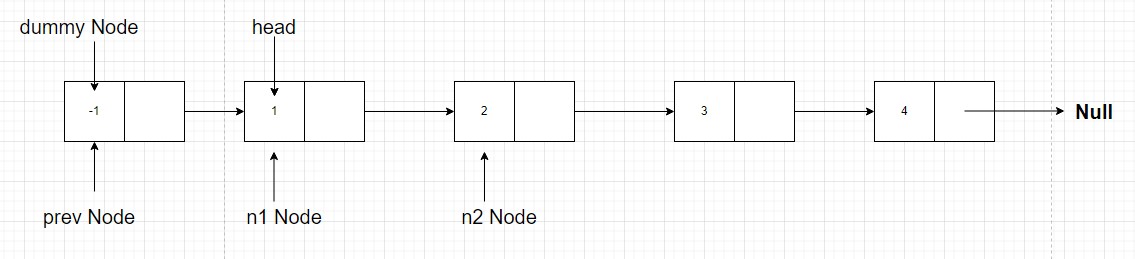
- Now the very first thing to do is change the
next pointer of prev node to point to n2 node. Why?? Because in the answer we want then2 node after dummy node. Right? So we will have to connectdummy node(now is prev node) to thenode with value 2(n2 node). The meansprev.next = n2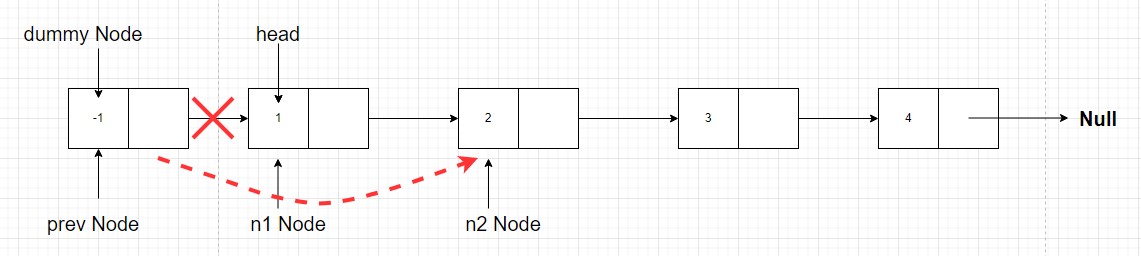
- Now in our final answer the
node with value 1should be at the place ofnode with value 2. So the next pointer ofnode with value 1should point to whatever thenode with value 2is pointing to originally. That means we will have to changen1 nextton2 nextn1.next = n2.next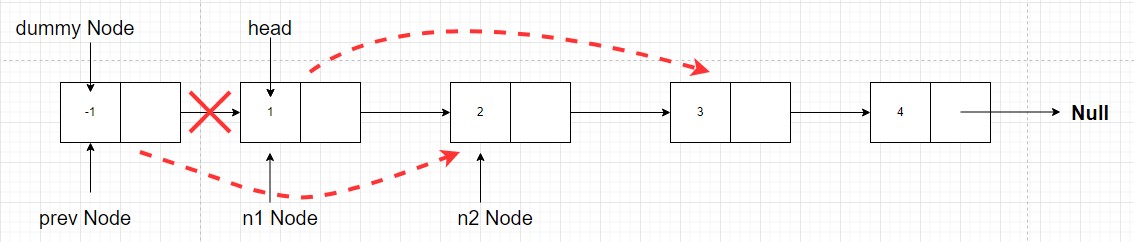
- Now as in the answer the
node with value 2should point tonode with value 1. That meansn2.next = n1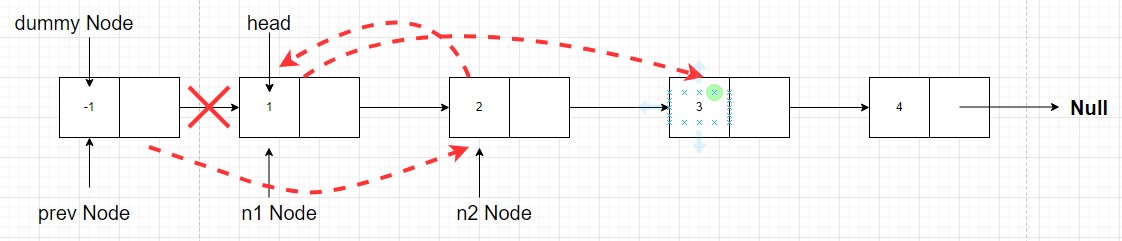
-
After this iteration, Nodes 1 and 2 will get swapped and our linked list will look like this
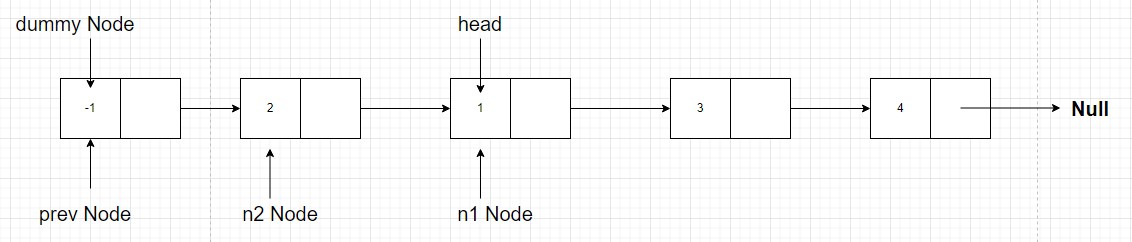
- Now for the next iteration, we have to swap
node with values 3 and 4. For that theprev nodeshould point tonode with value 1and thehead nodeshould point tonode with value 3. This meansprev = n1 head = n1.next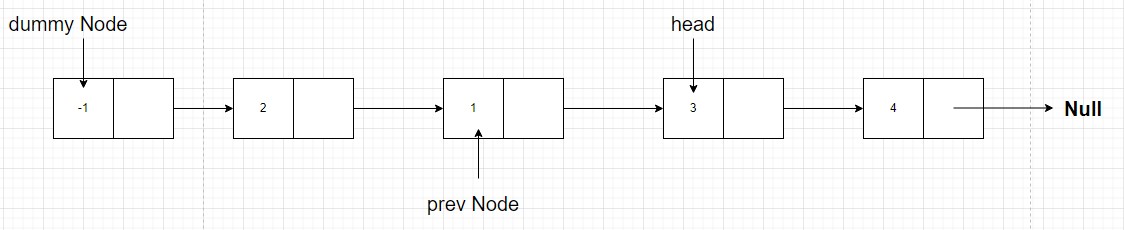
- We should stop this procedure when either there is no nodes left to swap or there is only one node left which cannot be swapped with any node.
- At the end, as we can see that our head of the list has been misplaced in the procedure of swapping, so we can return
dummy.nextto return the swapped linked list.
code
var swapPairs = function(head) {
// build a dummy nodes link to head, like [-1,1,2,3,4]
let dummy = new ListNode(-1)
dummy.next = head
// assign dummy to prev because prev will change to forward nodes, but dummy always link to first node, in this example is link to [2...]
let prev = dummy
// loop when head and head.next is not null
while(head && head.next) {
// cur node
let n1 = head
// next node
let n2 = head.next
// link to next node, first time is [2...]
prev.next = n2
// swap
n1.next = n2.next
n2.next = n1
// make prev move to forward node for next loop use, for example, first time prev assign to n1, when next loop prev.next like n1.next [1,3,4]
prev = n1
// change head is n1.next
head = n1.next
}
return dummy.next
};
Complexity: TC = O(n) SC = O(1)
Another solution: recursion
- First, we set some rules to stop recursion, if no current node or next node, stop recursion
if(!head || !head.next) return head - Now we make three variables that
v1represent current node andv2is next node andv3is node next thev2for recursionlet v1 = head let v2 = v1.next let v3 = v2.next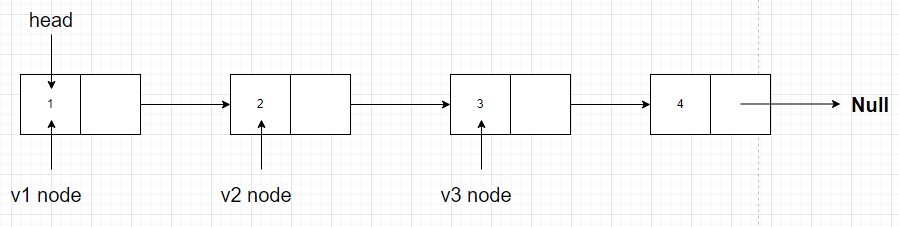
- Now we change
v2link tov1. And we assign recursionv3tov1. That meansv1.next = recursionFn(v3)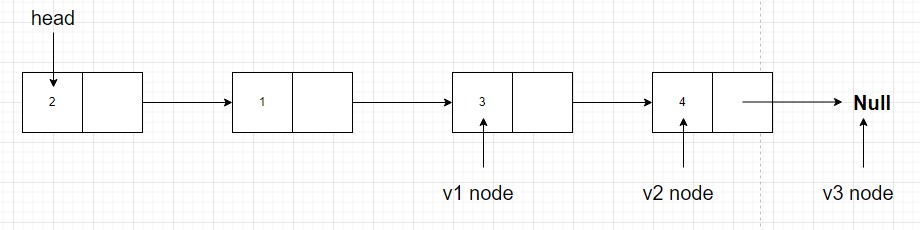
- Why do we always return
v2? Because after swap nodes, v2 represent the first node in the list, the first time isnode with value 2, the second time isnode with value 4
code
var swapPairs = function(head) {
// recursion terminator
if(!head || !head.next) return head
// process logic in current level
let v1 = head
let v2 = v1.next
let v3 = v2.next
v2.next = v1
// drill down
v1.next = swapPairs(v3)
return v2
}
Complexity TC = O(N) SC = O(1)